C#->condition and loop
1. if-else 语句
1.1 if 语句
if 语句是一个条件语句,当条件为真时执行一段代码。
if 语句的一般形式是:
if (判断条件)
{
// 当条件为真时,执行该语句
}条件可以是任何返回 true 或 false 的表达式。
例如:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 8;
int y = 3;
if (x > y)
{
Console.WriteLine("x 的值比 y更大");
}
}上面的代码将判断条件 x > y。 如果这是真的(即 x 比 y 大),if 块内的代码将被执行。
当 if 块中只有一行代码时,花括号可以省略。
例如:
if(x> y)
Console.WriteLine(“x比y大”);【填空题】将下面代码补充完整,实现当 age 大于 16 岁时,显示"welcome"
int age = 24;
__if_(age __>_ 16)
{
Console.WriteLine("Welcome");
}1.2 关系运算符
使用关系运算符来判断条件。 除(<)和大于(>)运算符之外,还有以下运算符可用:
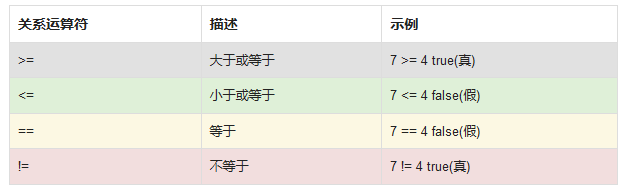
例如:
if (a == b) {
Console.WriteLine("等于");
}
// 如果a的值等于b的值,则显示等于【单选题】下列哪一个关系运算符是判断相等的? B.
A. ==
B. >=
C. <=
D. !=
1.3 else 分支
当 if 语句中的条件评估为 false 时,可以指定一个可选的 else 子句来执行一段代码。
语法:
if (判断条件)
{
//条件为真的时候执行
}
else
{
//条件为假的时候执行
}例如:
int mark = 85;
if (mark < 60)
{
Console.WriteLine("不及格");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("合格");
}
// 最终将输出 "合格"【填空题】将下面代码补充完整,输出 a 和 b 中较大的那个数
int a = 42;
int b = 88;
__if_ (a > b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
__else_
{
Console.WriteLine(__b_);
}1.4 if 嵌套语句
你也可以在 if 语句中嵌套 if 语句
例如:
int mark = 100;
if (mark >= 50) {
Console.WriteLine("合格");
if (mark == 100) {
Console.WriteLine("满分!");
}
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("不及格");
}
/*最终将会输出
及格
满分!
*/你也可以嵌套无限数量的 if-else 语句。
例如:
int age = 17;
if (age > 14) {
if(age > 18) {
Console.WriteLine("成人");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("青少年");
}
}
else {
if (age > 0) {
Console.WriteLine("儿童");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("年龄数值错误!");
}
}
//最终将会输出 "青少年"【填空题】下面程序执行以后将输出什么值?
int a = 8;
int b = ++a;
if(a > 5)
b -= 3;
else
b = 9;
Console.WriteLine(b);
//61.5 if-else if 语句
if-else if 语句可以用来决定三个或更多的动作。
例如:
int x = 33;
if (x == 8) {
Console.WriteLine("x 等于 8");
}
else if (x == 18) {
Console.WriteLine("x 等于 18");
}
else if (x == 33) {
Console.WriteLine("x 等于 33");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("没有找到对应值");
}
//输出 "x 等于 33"一个 if 可以有零个或者多个的 else if语句,但是必须在 else 之前
一旦其中的一个判断条件成功,则不会继续执行判断其他的条件
【单选题】一个 if 语句可以嵌套几个 if 语句? A.
A. 你想要几个都可以
B. 最多两个
C. 不可以嵌套
2. switch 语句
2.1 switch
switch 语句提供了一种更简单优雅的方式来判断变量与多个数值的相等情况,
每一个数值称作一个 case,当变量值与 case 相等时,条件为真,执行该 case 里面的方法
例如:
int num = 3;
switch (num)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("one");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("two");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("three");
break;
}
//输出"three"每个 case 代表一个要检查的值,后跟一个冒号,如果这个 case 匹配,那么这个语句会被执行。
switch 语句可以包含任意数量的 case。
注意:每个 case 语句执行结束都要使用 break 中止 switch 继续执行,否则,switch 会继续执行下面 case 的判断
在C#编程语言中,if else和switch都是用来进行条件分支的控制结构,但它们在用法和适用场景上有所不同:
2.2 default 语句
在 switch 语句中,可以添加一个 default 语句,他会在上述条件没有任何一个被匹配到的情况下执行
例如:
int age = 88;
switch (age) {
case 16:
Console.WriteLine("小孩");
break;
case 42:
Console.WriteLine("中年人");
break;
case 70:
Console.WriteLine("长辈");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("没有找到对应关系");
break;
}
// Outputs "没有找到对应关系"default 将会在没有匹配到条件时执行
将代码补充完整,实现输出 X 的值:
switch (x) {
case 10:
Console.WriteLine("Ten");
_break__;
case 20:
Console.WriteLine("Twenty");
break;
_default__:
Console.WriteLine("No match");.
break;
}2.3 break 声明
break 语句的作用是终止 switch 语句。
没有使用 break,即使 case 标签与变量匹配,执行以后仍会继续往下匹配 case 语句,直到结束或者遇到 break 语句。
所有 case 包括 default 都必须以 break 语句结束。
break 语句也可以用来跳过循环。 你将在后面的课程中学习到循环语句。
【单选题】如果我们忘记在 case 的末尾添加 break 语句,会发生什么? A.
A. 编译错误
B. 什么都不会发生
C. break 将被输出
3. 区别
if else 语句
- 灵活性高:
if else语句可以处理更为复杂的逻辑和条件判断,支持各种条件表达式,如比较运算符、逻辑运算符等。 - 结构:可以有单个
if,或者if后跟多个else if和一个else块,用于处理多重条件。 - 适用场景:适用于条件较为复杂或需要进行多个不同逻辑运算的场合。
switch 语句
- 简洁性:
switch语句通过一个表达式的不同值进行分支,每个分支用case标记,非常适合处理一个变量有多个具体值的情况。 - 结构:包括一个
switch表达式,多个case子句,以及可选的default子句。 - 适用场景:适用于需要根据单一变量的不同值做出决定的情况,特别是当这个变量有多个明确的值需要单独处理时。
switch常常被用于代替多个if else语句,使得代码更为整洁和易于理解。 - 限制:直到C# 7.0,
switch语句只支持整数、字符和字符串类型的简单比较。从C# 7.0开始,switch支持模式匹配,这使得它可以对类型和更复杂的数据结构进行判断。
性能考量
在大多数情况下,两者的性能差异不大,尤其是在现代编译器优化的背景下。对于大量的分支条件,switch语句可能会由于其内部优化(如跳转表)而有更好的性能。
示例
使用
if else:if (x < 10) { Console.WriteLine("小于 10"); } else if (x < 20) { Console.WriteLine("10 到 19"); } else { Console.WriteLine("20 或以上"); }使用
switch:switch (x) { case 10: Console.WriteLine("等于 10"); break; case 20: Console.WriteLine("等于 20"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("不是 10 也不是 20"); break; }
综上,选择if else还是switch主要取决于具体的应用场景和代码的可读性。在处理多个具体值的情况下,switch可能是更优的选择;而在需要复杂条件判断时,if else则更加合适。
4. 编程题目
4.1 if 语句练习题
- 基础比较:编写一个程序,接收两个整数输入,如果第一个数大于第二个数,则打印“第一个数大于第二个数”。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (a > b)
{
Console.WriteLine("第一个数大于第二个数");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("第二个数大于第一个数");
}
}- 温度警告:编写一个程序,接收温度(摄氏度)作为输入,如果温度高于30度,则打印“今天很热”。如果低于10度,则打印“今天很冷”。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int tem = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (tem > 30)
{
Console.WriteLine("too hot!");
}
else if (tem < 10)
Console.WriteLine("too cold!");
else
Console.WriteLine("good day");
}
}- 成绩分类:编写一个程序,根据输入的分数(0-100)输出学生的成绩等级。90以上为“A”,80-89为“B”,70-79为“C”,60-69为“D”,59以下为“F”。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int score;
Console.WriteLine("请输入你的分数");
score = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (score > 90 & score <100)
Console.WriteLine("A");
else if (score > 80 & score <90)
Console.WriteLine("B");
else if (score > 70 & score <80)
Console.WriteLine("C");
else if(score >60 & score <70)
Console.WriteLine("D");
else
Console.WriteLine("F");
}
}- 登录验证:编写一个程序,要求用户输入用户名和密码。如果用户名是“admin”且密码是“123456”,则打印“欢迎登录”,否则打印“用户名或密码错误”。????
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string name;
string password;
Console.WriteLine("请输入你的用户名:");
name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入你的密码:");
key = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (name == "admin" ) //怎么设置两个条件
Console.WriteLine("欢迎使用!");
}
}- 奇偶数判断:编写一个程序,输入一个整数,如果是奇数,打印“这是一个奇数”,如果是偶数,则打印“这是一个偶数”。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int num;
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (num % 2 == 0)
Console.WriteLine("这是一个偶数");
else
Console.WriteLine("这是一个奇数");
}
}4.2 switch 语句练习题
- 简单的日程安排:编写一个程序,根据用户输入的数字(1-7),输出对应的星期几。例如,1输出“星期一”,2输出“星期二”,以此类推。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int day;
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个数字(1-7)");
day = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch(day)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Monday");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Tuesday");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Wednesday");
break;
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("Thursday");
break;
case 5:
Console.WriteLine("Friday");
break;
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("Satuaday");
break;
case 7:
Console.WriteLine("Sunday");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("None!");
break;
}
}
}- 月份的天数:编写一个程序,接收月份号(1-12),输出该月的天数(不需要考虑闰年)。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int mon;
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个月份(1-12)");
mon = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch(mon)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("29");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("30");
break;
case 5:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("30");
break;
case 7:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 8:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 9:
Console.WriteLine("30");
break;
case 10:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
case 11:
Console.WriteLine("30");
break;
case 12:
Console.WriteLine("31");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("None!");
break;
}
}
}优化版本
using System;
class Program {
static void Main() {
// 读取用户输入的月份
int month = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
// 使用switch语句输出该月的天数
switch (month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
Console.WriteLine("31天");
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
Console.WriteLine("30天");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("28天");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("输入无效的月份");
break;
}
}
}- 用户角色:编写一个程序,根据用户输入的角色编码(例如:1代表管理员,2代表用户,3代表访客),打印相应的角色名称。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int dw;
Console.WriteLine("请选择你的角色编号:");
dw = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch(dw)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("调香师");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("小女孩");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("律师");
break;
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("幸运儿");
break;
case 5:
Console.WriteLine("病患");
break;
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("心理学家");
break;
case 7:
Console.WriteLine("玩具商");
break;
case 8:
Console.WriteLine("野人");
break;
}
}
}- 交通信号灯:编写一个程序,输入信号灯的颜色(红、黄、绿),输出对应的行动指示(例如红灯停,绿灯行,黄灯请注意)。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("输入当前信号灯状态:");
string TrafficLightCurrent = Console.ReadLine();
switch(TrafficLightCurrent)
{
case "Red":
Console.WriteLine("Stop!");
break;
case "Yellow":
Console.WriteLine("Slow down");
break;
case "Green":
Console.WriteLine("Free to go");
break;
}
}
}- 快餐菜单:编写一个程序,模拟快餐店的订单过程。用户输入菜单编号,根据编号显示对应的菜名和价格。
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("输入菜品编号:");
int num;
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch(num)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("鱼香肉丝 27¥");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("酸粉肥肠 58¥");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("农家小炒肉 30¥");
break;
}
}
}4.3 错题
登录验证:编写一个程序,要求用户输入用户名和密码。如果用户名是“admin”且密码是“123456”,则打印“欢迎登录”,否则打印“用户名或密码错误”。
using System;
class Program {
static void Main() {
// 读取用户名和密码
string username = Console.ReadLine();
string password = Console.ReadLine();
// 验证用户名和密码
if (username == "admin" && password == "123456") {
Console.WriteLine("欢迎登录");
} else {
Console.WriteLine("用户名或密码错误");
}
}
}5. while 循环
逻辑运算符可用于控制循环运行的次数。 例如:
int num = 1;
while(num < 6)
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
num+=2;
}
/* 输出
1
3
5
*/如果最终没有使循环条件为 false 的语句,则循环将无限循环执行,我们称之为"死循环"。
【填空题】显示 0 到 100 内的所有偶数
int num = 0;
while (_num__ < 100)
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
num _+__ = __2_;
}5.2 while 循环条件控制
我们也可以通过在循环条件中递增 num 的值来控制循环,例如:
int num = 0;
while(++num < 6)
Console.WriteLine(num);思考一下,while (num ++ <6) 和 while (++num < 6) 之间有什么区别吗?
当然是有的啦! 循环 while (++num <6) 将执行 5 次,因为先自增了 num 的值再判断 num < 6 的条件,而 while (num ++< 6) 因为先执行再自增 num 的值,所以将会执行 6 次。
【单选题】该循环将被执行几次?
int x = 1;
while (x++ < 5)
{
if (x % 2 == 0)
x += 2;
}两次。
6. for 循环
6.1 for 循环
for 循环以特定的次数执行一组语句,具体语法如下:
for (单次表达式;条件表达式;末尾循环体) {
中间循环体
}
/*
单次表达式:在循环开始之前执行,且只执行一次
条件表达式:循环是否执行的判断条件
末尾循环体:每次循环结束以后执行的
中间循环体:每次循环要执行的代码
*/for 循环的执行顺序为:
先执行单次表达式,声明需要的变量,然后判断条件表达式,满足条件则进行中间循环体,最后执行末尾循环体。
需要注意的是,执行完末尾循环体以后,不会再执行单次表达式,而是直接进行条件判断,如果满足条件表达式,则继续进行循环,直到条件不满足条件表达式,通过下面的实例,我们会更容易理解一些:
for (int x = 10; x < 15; x++)
{
Console.WriteLine("x的值是: {0}", x);
}
/*输出结果为
x的值是: 10
x的值是: 11
x的值是: 12
x的值是: 13
x的值是: 14
*/注意 for 循环条件中使用的是分号
【选词填空】选择填空,创建一个完整的 for 循环
for (___;___;___)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}6.2 通过算数运算符控制 for 循环
算术运算符可用于控制循环次数,例如:
for (int x = 0; x < 10; x+=3)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
/* 输出
0
3
6
9
*/当然,用减法也是可以的
for (int x = 10; x > 0; x -= 2)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
/* 输出
10
8
6
4
2*/【填空题】使用 for 循环,打印 0-100 的偶数值
_for_ (int x = 0; x < 100; x+= _2__)
{
Console.WriteLine(__x_);
}6.3 for 循环允许的空参数
如果不需要,可以省略单次表达式和末尾循环体语句,但是请记住,分号是强制性的。
例如,省略单次表达式:
int x = 10;
for ( ; x > 0; x -= 3)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}又或者,末尾循环体语句一起省略:
int x = 10;
for ( ; x > 0 ; )
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
x -= 3;
}
for(;;){}是一个无限循环。
【填空题】下面的 for 循环会执行几次?
int x = 1;
for ( ; x < 7; )
{
x+=2;
}三次
7. do-while 循环
7.1 do-while 循环
do-while 循环类似于 while 循环,不同的是,do-while 先执行语句再判断循环条件,所以 do-while 循环保证循环体至少执行一次。
例如:
int a = 0;
do {
Console.WriteLine(a);
a++;
} while(a < 5);
/* 输出
0
1
2
3
4
*/注意 while 语句之后的分号。
【填空题】填空创建一个有效的 do-while 循环。
int x = 0;
__do_ {
Console.WriteLine(x);
x+=2;
}_while__(x < 10) _;__7.2 do-while 和 while 的区别
即使 do-while 循环的条件判断结果为 false,do 中的语句仍然会运行一次:
int x = 42;
do {
Console.WriteLine(x);
x++;
} while(x < 10);
// 输出 42do-while 循环至少执行一次语句,然后再判断条件,即先执行,后判断。
while 循环只有在判断条件成立之后才执行语句,即先判断,后执行。
【填空题】以下代码,最终输出的结果是?
int a = 2;
do {
a+=3;
} while(a < 4);
Console.Write(a);
//output 58. 结束循环 break 和 continue
8.1 break 语句
我们在 switch 语句中看到了 break 的作用。
break 的另一个用途是在循环中:当循环中遇到 break 语句时,循环会立即终止。
int num = 0;
while (num < 20)
{
if (num == 5)
break;
Console.WriteLine(num);
num++;
}
/* 输出:
0
1
2
3
4
*/如果使用嵌套循环(即在另一个循环内有一个循环),break 语句将停止最内层循环的执行,并开始执行块之后的下一行代码。
【填空题】下列代码执行后,打印出的最大数值是?
for (int x = 1; x < 8; x++) {
if (x > 5)
break;
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
1
2
3
4
58.2 continue 语句
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5)
continue;
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
/* 输出:
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
*/正如你所看到的,数字 5 不会被输出,因为 continue 语句会跳过本次循环。
【填空题】填写空白处,使下列代码输出偶数:
for(int x=0; x<99; x++) _{__
__if_ (x%2 != 0)
___continue;___
Console.WriteLine(x);
}9. 逻辑运算符
9.1 逻辑运算符
逻辑运算符用于连接多个表达式,返回 true 或 false。
| 逻辑运算 | 逻辑运算名 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
&& | 与 | y && y |
|| | 或 | x || y |
! | 非 | !x |
&& (与) 的判断方式如下:
| 左边 | 右边 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| false | false | false |
| false | true | false |
| true | false | false |
| true | true | true |
例如,如果您希望仅在年龄大于 18 且金额大于 100 时才在屏幕上显示文本:
int age = 42;
double money = 540;
if(age > 18 && money > 100) {
Console.WriteLine("Welcome");
}"与"运算符用于组合这两个表达式。
用"与"逻辑运算符,两个操作数必须同时为真,才能使整个表达式成立。
【单选题】要使 a&&b 的结果为 true, B.
A. a 和 b 都必须为 false
B. a 和 b 都必须为 true
C. 只要 a 和 b 有一个为 true
D. 任何情况都不可能
9.2 "与"(&&)的逻辑运算
你可以使用两个以上的"与"(&&)运算符
int age = 42;
int grade = 75;
if(age > 16 && age < 80 && grade > 50)
Console.WriteLine("Hey there");只有当所有的条件都是真的时,整个表达式的判断结果才为真。
【问题】一个判断最多可以使用几个"与"(&&)运算呢? 任意。
9.3 "或"(||)的逻辑运算
"或"(||)的逻辑运算,左右两边,只要有一个条件为真,则其运算结果为真。具体可参照下表:
| 左边 | 右边 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| false | false | false |
| false | true | true |
| true | false | true |
| true | true | true |
示例:
int age = 18;
int score = 85;
if (age > 20 || score > 50) {
Console.WriteLine("Welcome");
}和"与"(
&&)的逻辑运算一样,你可以使用任意数量的"或"(||),甚至,多个"或"(||)和"与"(&&)语句可以合在一起使用。
下面代码最终输出的结果是?
int x = 5; int y = 12;
if(x>10 || y/x > 1)
Console.Write(y-x);
else
Console.Write(y);
//output 129.4 "非"(!)的逻辑运算
"非"(!)的逻辑运算符只用一个操作符,作用是反转其逻辑状态。例如,如果条件成立,则"非"(!)的逻辑运算以后该条件的返回结果为假,反之亦然。
| 右边 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| true | false |
| false | true |
示例:
int age = 8;
if ( !(age >= 16) ) {
Console.Write("您还不满16周岁!");
}
// 输出: "您还不满16周岁!"如果 a 是真的,b 是假的,那么 !(a && b) 的结果是什么?
真的。
10. 三元运算符
10.1 三元运算符
我们还是通过实例来讲解三元运算符吧,思考一下下面的实例:
int age = 42;
string msg;
if(age >= 18)
msg = "Welcome";
else
msg = "Sorry";
Console.WriteLine(msg);上面的代码判断年龄变量的值并将相应的消息显示在屏幕上。
使用三元运算符可以更简洁优雅的表达这个这段代码。三元运算符的格式如下:
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
三元运算符的判断顺序为:先判断Exp1的条件,如果Exp1为真,则执行Exp2,否则,执行Exp3。所以,上述代码使用三元运算符的写法如下:
int age = 42;
string msg;
msg = (age >= 18) ? "Welcome" : "Sorry";
Console.WriteLine(msg);执行以下代码,x 的值是?
int x = 5;
int y = 3;
x = (x > y) ? y : x;
x的值是311. 基础运算
11.1 基础运算
现在让我们创建一个简单的项目,反复要求用户输入两个值,然后显示它们的总和,直到用户输入退出。
我们从一个 do-while 循环开始,要求用户输入并计算总和:
do {
Console.Write("x = ");
int x = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("y = ");
int y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int sum = x+y;
Console.WriteLine("Result: {0}", sum);
}
while(true);上面的代码会无限循环,我们还需要处理退出事件。
用户也有可能输入一个非整数值导程序在数值类型转换的时候出错。用户的输入是不安全的,我们也将在下面的课程中学习如何处理这一类异常。
下面的循环将会执行几次?
do { }
while(false);执行一次。
11.2 基础运算
如果我们希望用户输入“exit” 的时候可以退出程序循环,那我们可以使用一个 break 语句:
Console.Write("x = ");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str == "exit")
break;
int x = Convert.ToInt32(str);在上面的代码里,我们对用户的输入值进行了判断,如果用户输入的值是"exit",则退出循环。
所以完整的整个程序应该是:
do {
Console.Write("x = ");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str == "exit")
break;
int x = Convert.ToInt32(str);
Console.Write("y = ");
int y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int sum = x + y;
Console.WriteLine("Result: {0}", sum);
}
while (true);【单选题】以下哪个方法是用于获取用户输入的?
A. Console.Write
B. Convert.ToInt32
C. Console.ReadLine ✅
12. 模块二测验
- 【填空题】填空,实现打印 x 的值五次
int x = 42;
int num = 0;
while(num < __5_ ) {
Console.WriteLine(_num__);
_num__ ++;
}- 创建一个有效的 for 循环
_for__(_int x =_0_;_X < 10__;_x ++__) {
Console.WriteLine(x);
}- 【多选题】下面关于"与"(
&&),"或"(||),"非"(!)的描述,哪些是正确的?AD
A. c 为真(true),则 (a&&b)||c 也为真(true)
B. a&&b为真(true),只要 a 或者 b 其中一个条件为真(true)就可以
C. a 和 b 都为真(true),则 a&&b 为假(false)
D. a||b为真(true),只要 a 或者 b 其中一个条件为真(true)就可以
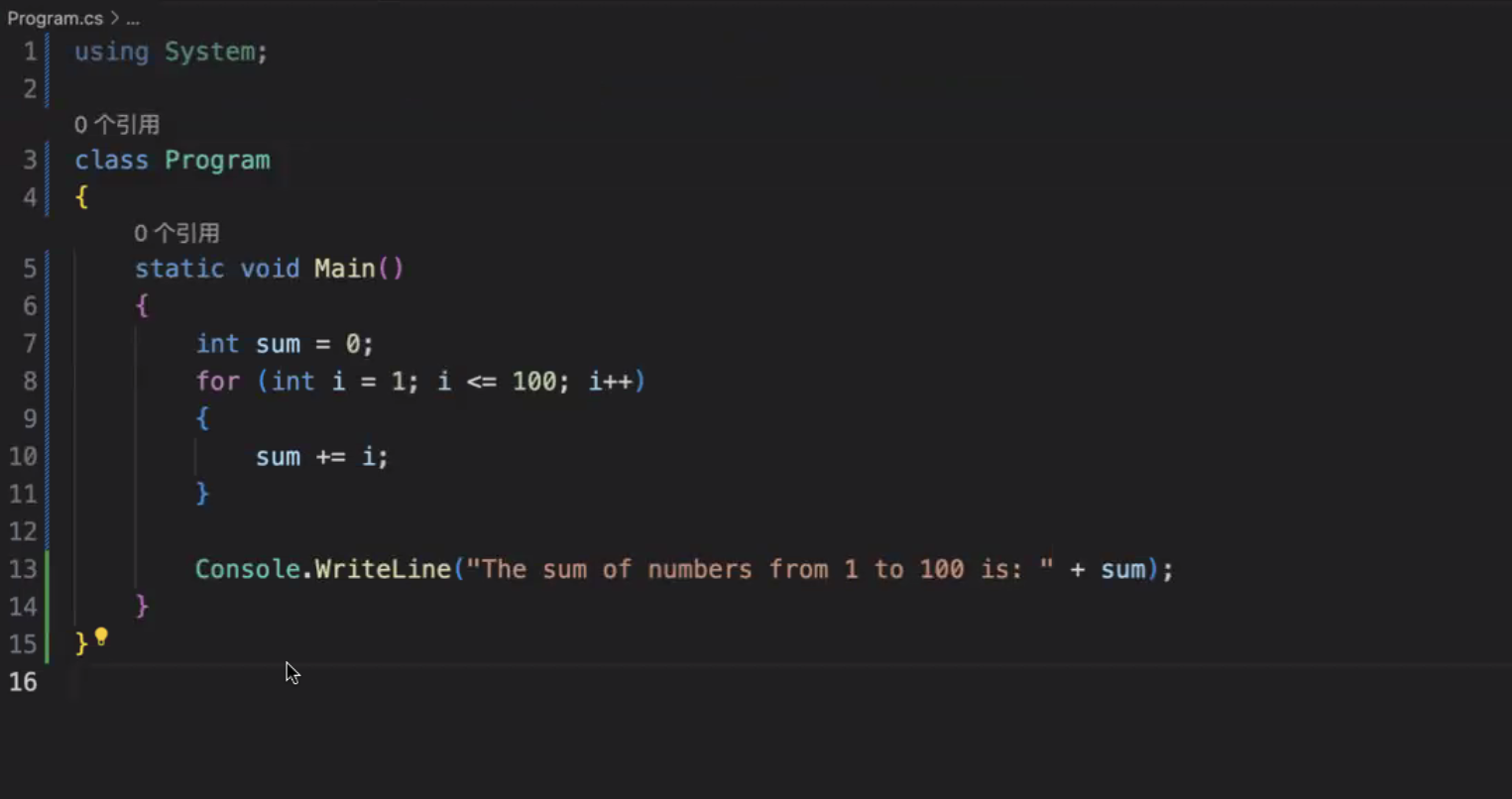
- 编写程序计算 1 到 100 所有整数的总和;
- 执行完以下代码后,x 的值是?
int x = 4; int y = 9; x = (y%x != 0) ? y/x : y;
- 99乘法表

image-20240429102515535
