Coventry-Class 02
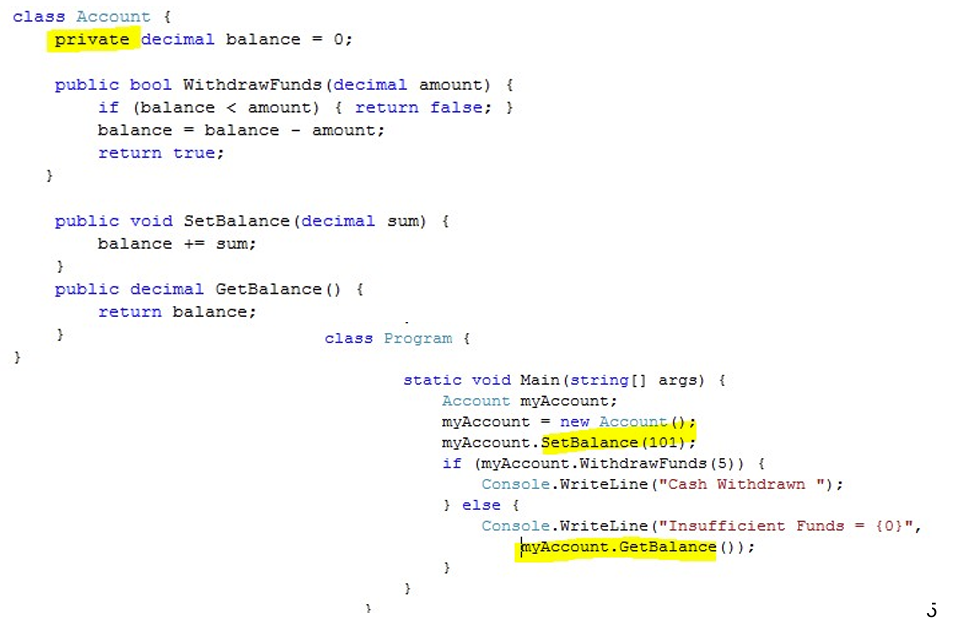
1. public Methods
• This means that code running outside the class can make calls to that method
• This has got to be the case, since we want people to interact with our objects by calling methods in them.
• In general the rules are:
–if it is a data member (i.e. it holds data) of the class, make it private
–if it is a method member (i.e. it does something) make it public
这意味着在类外运行的代码可以调用该方法
情况必须如此,因为我们希望人们通过调用对象中的方法来与我们的对象交互。
一般来说,规则如下
-如果它是类的数据成员(即保存数据),则将其私有化
-如果是方法成员(即执行某些操作),则将其设置为公共成员
2. Static Items
• All the members that we have created in our class Account have been part of an instance of the class
• One can create members which are held as part of the class, i.e. they exist outside of any particular instance
• The static keyword lets us create members which are not held in an instance, but in the class itself
我们在类账户中创建的所有成员都是类实例的一部分
我们可以创建作为类的一部分的成员,即它们存在于任何特定实例之外。
通过 static 关键字,我们可以创建不存在于实例中,而是存在于类本身的成员
2.1 Static vs const
• Note that we have made the data member of the class static, so that it is part of the class and not an instance of the class.
• One common programming mistake is to confuse static with const
–Marking a variable as const means ―the value cannot be changed
–Marking a variable with static means ―the variable is part of the class and is always present
请注意,我们将该类的数据成员设置为静态,因此它是该类的一部分,而不是该类的实例。
一个常见的编程错误是混淆 static 和 const
-将变量标记为 const 意味着 - 变量值不可更改
-将变量标记为 static 意味着 - 变量是类的一部分,始终存在
2.2 共享Main函数
- AccountTest class 有一个名为 Main() 的静态成员方法
- 如果我们创建 50 个 AccountTest 实例,它们都将共享相同的 Main() 方法
- 在 C# 中,关键字 static 将成员标记为类的一部分,而不是类实例的一部分。

•We don't have to make an instance of the AccountTest class to be able to use the Main() method
• Keyword static doesn’t mean “cannot be changed”
• Members of a class which have been made static can be used just like any other member of a class • Either a data member or a method can be made static
-我们不必创建 AccountTest 类的实例就能使用 Main() 方法
关键字 static 并不意味着 "不能更改"。
静态化后的类成员可以像其他成员一样使用 - 数据成员或方法都可以被静态化
2.3 Using a static data member of a class
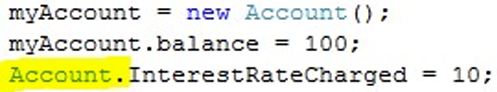
下面这个关于银行利率的代码:
• The interest rate is held for all the accounts. • If the interest rate charged it must be charged for all accounts.
- 所有账户都有利率。 - 如果收取利率,则必须对所有账户收取。

我们可以这么解决这个问题:

现在,这个利率是类的成员而不是实例的成员。我们要通过调用类的方法调用它。
2.4 Using a static method in a class
什么情况下用Static Method??
Example:
我们可以根据某人的年龄和收入来决定是否允许其拥有银行账户。
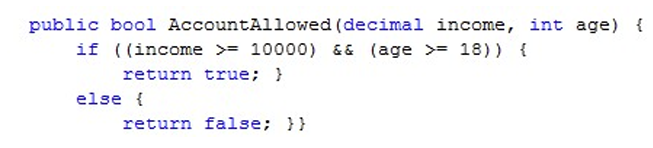
这时我们要有了一个实例(账户)后才能调用该方法。但是我们不想这样。我们想调用这个实例并被允许后,才能激活满足条件的实例(账户)。
•We can't call the method until we have an Account instance. •We can solve this by making the method static
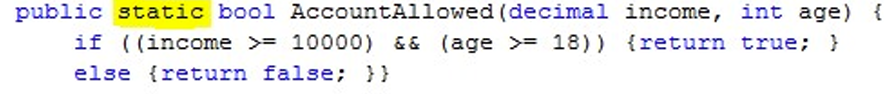
现在这个方法是类的一部分,不属于任何实例;
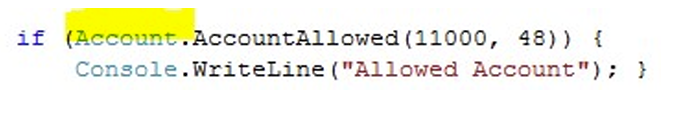
2.5 Using member data in static methods
using System;
namespace Program
{
class Account
{
private decimal myaccount;
private int myage;
public static bool AccountAllow(decimal income,int age)
{
if (income >= 10000 && age > 18)
{
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
}这也就是说,在创建新实例之前,要经过AccountAllow的“考验”。我们称之为“构造函数”。
3. Construction of Objects
什么时候用构造方法?
当创建一个类的实例时,C# 系统会调用该类的构造方法。
构造方法的作用是什么?
构造方法是类的一个成员,它可以让程序员控制和设置新对象的内容
如果没有已定义的构造函数?
编译器会为我们创建一个默认构造函数并使用它。
3.1 Default Constructor
• A constructor method has the same name as the class, but it does not return anything:
• Default constructor is public so that it can be accessed from external classes who might want to make instances of the class.
• It accepts NO parameters.
构造方法与类的名称相同,但不返回任何内容:
默认构造函数是公开的,这样外部类就可以访问该构造函数,从而创建该类的实例。
它不接受任何参数。
像这样:
class Account
{
public Account()
{
}
}3.2 Defined constructor 已定义的构造函数
class Account
{
private string name;
private string address;
private decimal balance;
public Account(string inname,string inaddress, decimal balance)
{
name = inname;
address = inaddress;
balance = inbalance;
}
}只有当程序员没有提供构造函数时,编译器才会提供默认构造函数。
4. Overloading Constructors
"A method has the same name as another, but has a different set of parameters"
Overloading a method name
我们可以重载类中的任何方法名称。如果您有一个特定的操作可以由多个不同的数据项驱动,例如设置交易日期的多种方法,这将非常有用:

5. access modifiers
–public: type or member can be accessed by any other code in the same assembly or another assembly that references it
–private: type or member can be accessed only by code in the same class or struct
–protected : type or member can be accessed only by code in the same class or struct, or in a class that is derived from that class
– private protected: type or member can be accessed by types derived from the class that are declared within its containing assembly. 类型或成员可被包含在类的程序集中声明的类派生类型访问。(同程序集)
– internal : type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, but not from another只能从同一个程序包访问。
– protected internal : type or member can be accessed by any code in the assembly in which it is declared, or from within a derived class in another assembly 可被访问该程序包或者别的程序包的派生类访问
6. Lab
- Code an example of a traffic light controller that uses the following enumerator:
enum TrafficLight { Red, Green, Amber };
using System;
// 定义一个枚举,代表交通信号灯的三种状态:红灯、绿灯、黄灯
enum TrafficLight { Red, Green, Amber }
class TrafficLightController
{
// 定义一个私有变量来存储当前的信号灯状态
private TrafficLight currentLight;
// 构造函数,初始化交通信号灯状态为红灯
public TrafficLightController()
{
currentLight = TrafficLight.Red;
}
// 方法:改变信号灯的状态
public void ChangeLight()
{
// 使用switch语句来根据当前的信号灯状态切换到下一个状态
switch (currentLight)
{
case TrafficLight.Red:
currentLight = TrafficLight.Green; // 红灯变绿灯
break;
case TrafficLight.Green:
currentLight = TrafficLight.Amber; // 绿灯变黄灯
break;
case TrafficLight.Amber:
currentLight = TrafficLight.Red; // 黄灯变红灯
break;
}
// 输出当前的信号灯状态
Console.WriteLine($"当前信号灯状态: {currentLight}");
}
}
class TestTrafficLightController
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建TrafficLightController的实例
TrafficLightController controller = new TrafficLightController();
// 模拟信号灯变化
controller.ChangeLight(); // 切换一次信号灯
controller.ChangeLight(); // 再切换一次
controller.ChangeLight(); // 再切换一次
}
}- 编写一个著名的 "Hello World "程序的面向对象版本。您的版本应包括一个封装问候语字符串的类,并具有以下功能: - 带有问候语 "Hello World "的默认构造函数 - 带有字符串参数的构造函数,用于指定问候语 - SetGreeting() 和 GetGreeting() 方法,用于在对象构造完成后指定该对象的问候语,并相应地显示当前的问候语 您应提供一个测试类,以演示其功能 注释供自己参考。
using System;
class WarmWords
{
private string Greeting;
public WarmWords()
{
Greeting = "Hello World";
}
public WarmWords(string greeting)
{
Greeting = greeting;
}
public string Getgreeting()
{
return Greeting;
}
public void SetGreeting(string greeting)
{
this.Greeting = greeting;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WarmWords warmwords1 = new WarmWords();
Console.WriteLine(warmwords1.Getgreeting());
warmwords1.SetGreeting("你好");
Console.WriteLine(warmwords1.Getgreeting());
}
}