Agile 01
1. The Beginning of Software Development
1.1 Bad Practices
• Presence of typos in the code 错字
• No proper structure and formatting of the code 没有正确的代码结构和格式
• No use of comments in the code 注释
• No accurate declaration of values 对值的声明要准确
• Use of magic numbers 魔术数字不能用
• Logic errors in the code 逻辑错误
• Complex and lengthy code 冗余复杂的代码
• Non-modular code 代码没有模块化
1.2 key DEVELOPMENT practices
• Validation of input
• Error Handling and Logging
• Database security
• Memory management
• Data protection
• Types verification
1.3 Life Cycle
• Planning: Provides a project management plan that works as the basis for acquiring the resources needed to develop the considered system. 获取并规整资源
• Requirements/Analysis: Specifies user requirements describing the detailed functioning of the intended system. 了解用户对于软件的功能需求。
• Design: System features and operations are described in detail(i.e. system requirements) through the use of prototype models like process diagrams,pseudo codes,etc. 通过使用流程图、伪代码等原型模型,详细描述系统功能和操作(即系统需求)。
• Development: the system is constructed involving the actual programming process. 写代码
• Testing: Demonstrates that the system conforms to requirements by applying testing techniques.
• Maintenance: the system is assessed/evaluated to ensure it does not become obsolete. This is also where changes are made to initial system functioning. 确保系统功能不过时。也包括维护和检修?
1.4 一些其他software design Approach
1.4.1 Waterfall
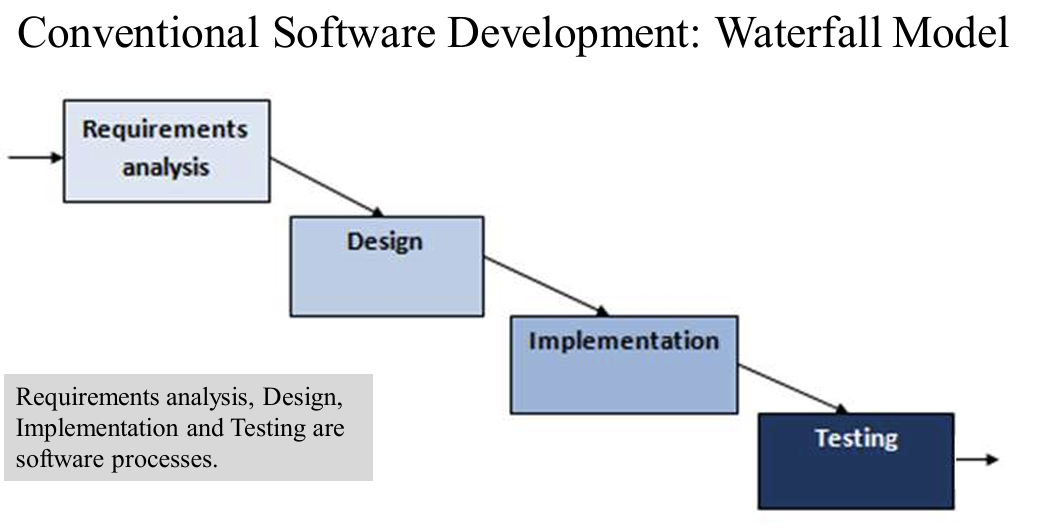
Problems associated with Waterfall model:
−Allows a sequential flow of activities from completion of a phase to the next
−Unable to accommodate the nature of uncertainty of project’s requirements. It is difficult for customers to identify detailed criteria at the beginning of the project. Revision of requirements is difficult.
−Software development can be a long process which does not produce a working version of the system until late in the process.
−product usually is not available for customer’s feedback until the end of the development, thus high risk
瀑布模型的相关问题:
-允许从一个阶段完成到下一个阶段的活动顺序流
-无法适应项目要求的不确定性。客户很难在项目开始时确定详细的标准。需求修订困难。
-软件开发可能是一个漫长的过程,直到后期才会产生系统的工作版本。
-产品通常要到开发后期才能得到客户的反馈,因此风险很高。
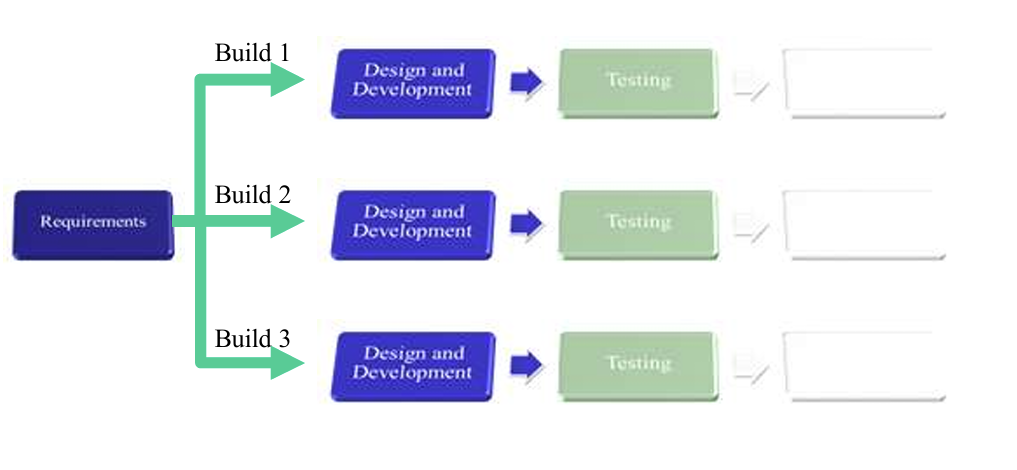
1.4.2 Iterative Approach
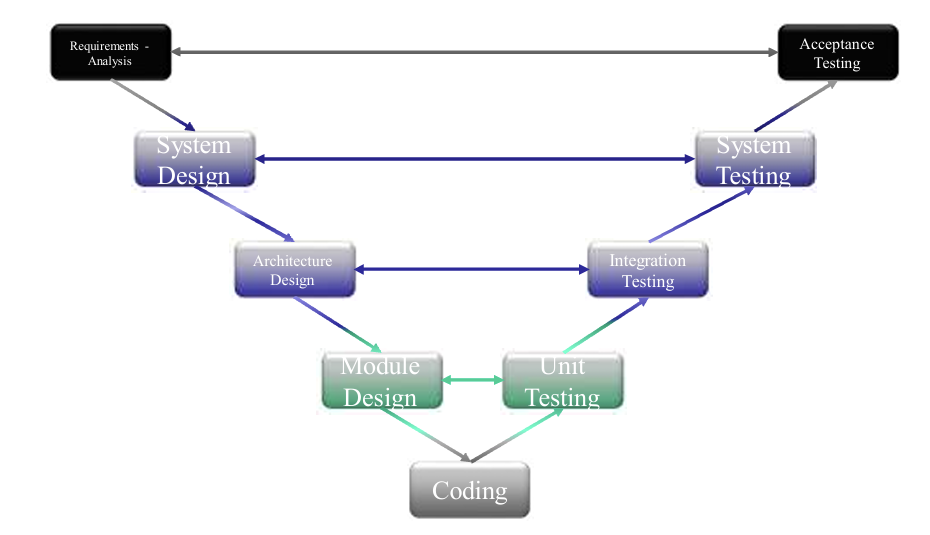
1.4.3 V-model Approach
2. Agile
2.1 some of the features
Proposes incremental and iterative approach to software design
Gives less priority on documentation than software development
Allows self-organizing teams to respond to change
Enables errors to be fixed in the middle of the project.
Enables the customer to have early and frequent opportunities to give feedback on the product and make decision and changes to the project
Requires close communication with developers and together analyse requirements and planning
Delivers shippable features of the product to the customer at the end of an iteration.
Implements small projects very quickly
Allows iterative development process to execute a project in short (2-4) weeks iterations.
Allows implementing regression testing every time new functions or logic are released in each iteration.
核心特点:
提出软件设计的增量和迭代方法
对文档的重视程度低于软件开发
团队应对需求变化简单:
允许自组织团队应对变化
可在项目中期修复错误
客户(提出的需求实现):
让客户有机会尽早、频繁地对产品提出反馈意见,并对项目做出决策和修改
需要与开发人员密切沟通,共同分析需求和规划
在迭代结束时向客户交付可交付的产品功能。
实施项目快速:
快速实施小型项目
允许迭代开发流程在短期内(2-4 周)迭代执行项目。
测试性:
允许在每次迭代中发布新功能或逻辑时实施回归测试。
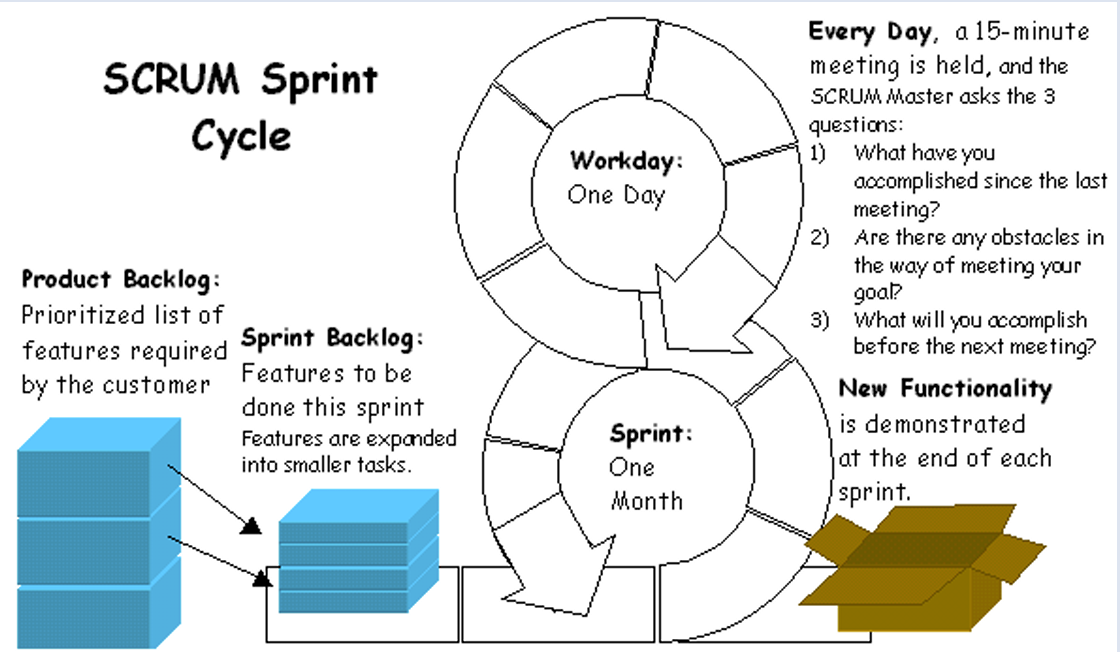
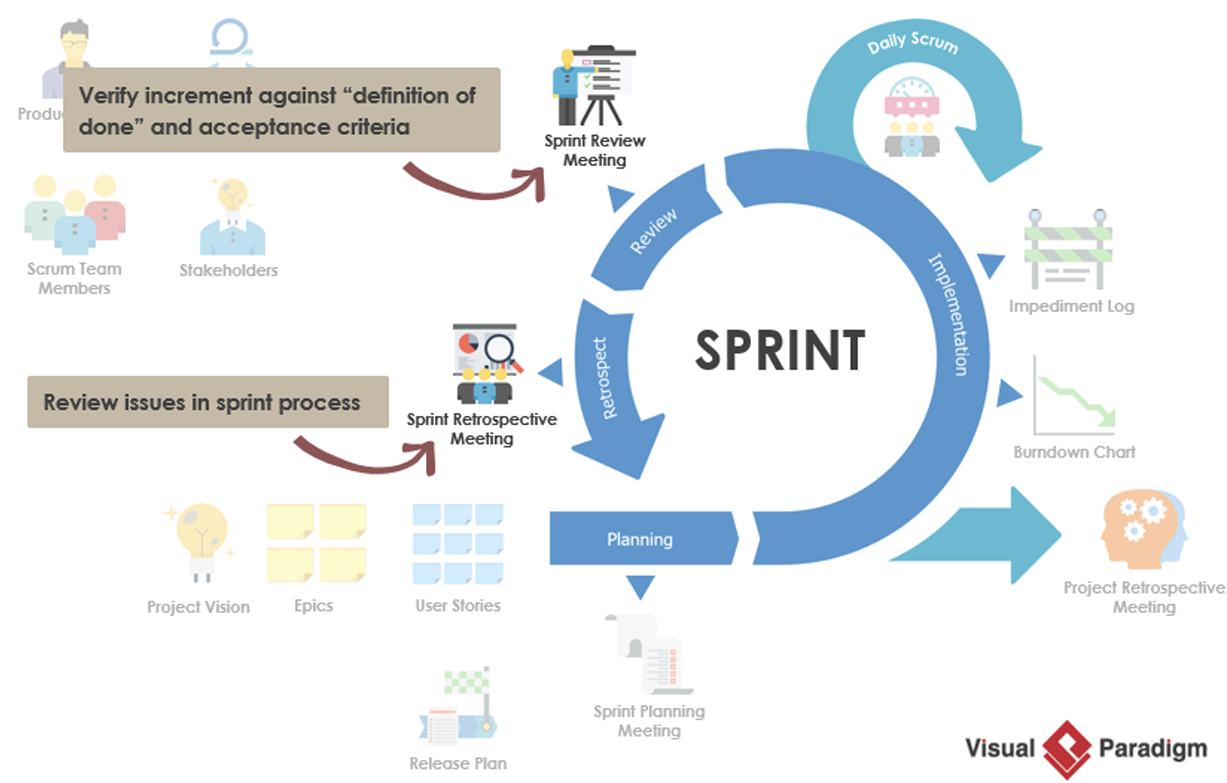
2.2 Scrum
2.2.1 Roles
• product owner:
✓ knows what the customer wants and can then translate the customer's needs back to the Scrum team
与客户沟通需求。
✓ must have the authority to make all decisions necessary to complete the project
有权作出完成项目所需的所有决定
✓ is responsible for identifying product features, translating them into a prioritised list (i.e. Product Backlog), prioritising the list for the next Sprint (i.e. Sprint Backlog), and continually re-prioritising and refining the list
负责确定产品功能,将其转化为优先级列表(即 Product Backlog),为下一个 Sprint 确定列表的优先级(即 Sprint Backlog),并不断重新确定和完善列表的优先级
✓ works with customers and stakeholders as well as working with the Team implementing the Product Backlog.
与用户和股东和开发人员协商
• scrum master: A person who works closely with the team, sometimes as a member: e.g.
✓ to guide the team in Scrum practices
✓ to ensure the team understands and adhere to best Scrum practices
✓ to facilitate the Scrum ceremonies
✓ to coach the team to self-organise and self-manage
✓ to make sure the team is cross-functional
✓ to keep the team focused on a transcendent goal
✓ to assist the Product Owner to refine a ready backlog
✓ to keep team in high morale
• development team: a team of software developers plus, other scrum roles, stakeholders and users of software products
2.2.2 Scrum events:
• Sprint planning meeting • Daily scrum meeting • Sprint review meeting • Sprint retrospect meeting
2.2.3 Artifacts:
• Product backlog • Sprint backlog • Increment (i.e., working features)
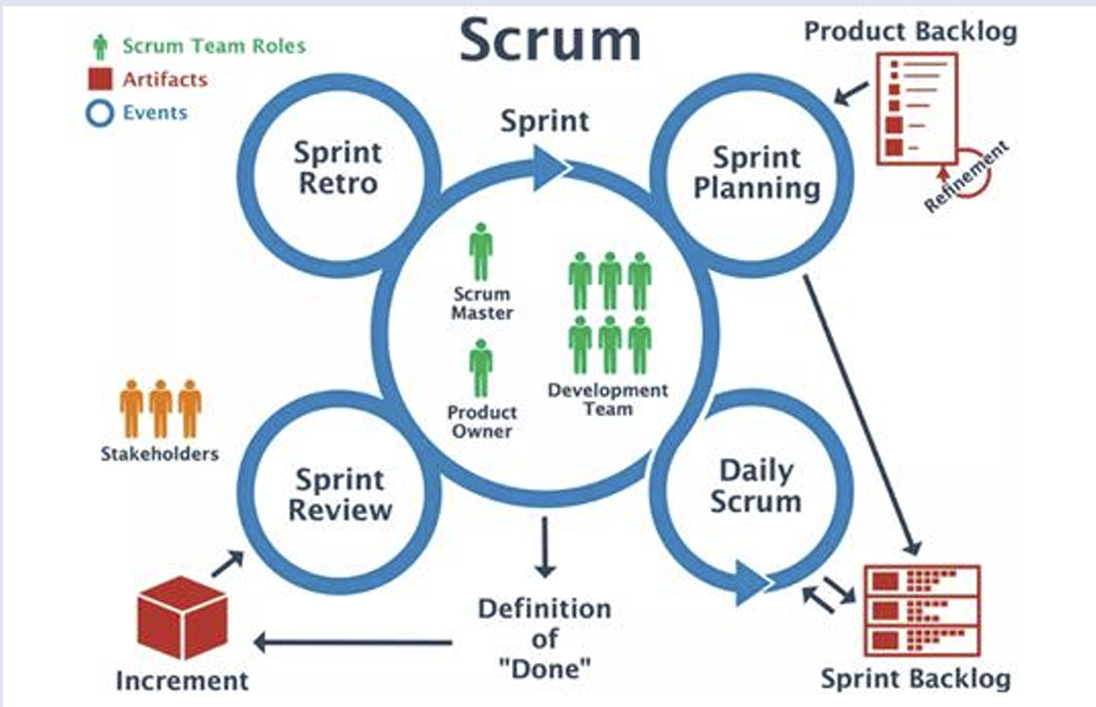

2.3 Kanban
−define and visualize policies (process rules or guidelines) explicit and visualises the flow of work on a Kanban board that contains the process steps to deliver work
可视化的工作流程,包含交付工作的流程。
−Applies Limiting work-in-progress (WIP), which to ensure the work currently in progress to be completed before taking up new work
在完成当前工作前不可以进行新工作
−continuous development and delivery, tackling a small number of tasks concurrently -持续开发和交付,同时处理少量任务
−Suitable for the software team with a continuous stream of work requests -适用于工作请求源源不断的软件团队
2.4 Extreme programming (XP)
- −Pair-wise programming: demands that each and every line of code is developed by a pair of programmers. The work in these pairs involves a division of labour in which one person is actively involved in the actual generation of code, while the other takes a supporting and reviewing role.
分工合作工作,一个写代码,一个辅助加审查。
- −Relies on constant code improvement, user involvement in the development team and pair wise programming.
“三大特色”
- Feature:
−Supports change through small, frequent system releases
−full-time customer engagement with the team. 用户全程参与
−maintaining simplicity through constant refactoring of code 不断重构代码
−emphasizes final product
−test based approach to requirements and quality
−lightweight methods suit small-medium size projects 适合小型企业
2.5 Test Driven Development (TDD):
a specific engineering practice from XP
- Life Cycle:
- Write the test for a new feature (function or requirement through user stories)
- Run the test and see if the new test fails
- Write the code that pass the test that fails
- Refactor code: improve code
- Repeat the above process
TDD vs. Agile:
TDD and agile both adopt an interactive and incremental process
Differences:
-TDD focuses on how code is written and tested, whereas agile focuses on the overall development process
-TDD focuses on how code is written and tested by a given developer, whereas agile focuses on groups of developers
2.6 Kanban Board
concepts: consisting of notes for tasks on the physical or electronic board as follows:
就是说像Kanban Approach一样把工作写在人人可见的看板上
e.g. −To Do: lists the tasks that are not yet started. (i.e., backlog) −Doing: the tasks that are in progress −Done: the tasks that are completed

- Scrum Board: Many Scrum teams also adopt select principles of Kanbanas a visual process tool
−To track work in Sprints (i.e., short, consistent and repetitive periods of time). A set of tasks need to be completed in each sprint in which no new activities are allowed to be added)
3. User Story
- as a < Type of user >, I want to < perform some Tasks >, so that < achieve some goal >
Examples :
As an administrator I want to be able to create a new user to the team when needed. As a user I want the ability to restore my password.
As a cashier I want to see total amount in cash register displayed.
As a credit card user I want to be warned if spent more than a set amount.
As a ticket booker I want to be notified as soon as a ticket gets available on a full flight.
User Story: As a University student, I want to see my modules for a semester, so that I know what to study.
• Acceptance Criteria: e.g. The modules for each semester is displayed. A different semester can be selected. The module are not displayed if the student fails to login.
