OO conception
1. class and Object
1.1 Conception
class
encapsulates(封装) attributes(Python variables) and operations (Python method) into a single entity,which describes a set of data and the operations that will act on data.
object
is an instance of a class and has the properties(属性) and behaviour of it class.
Unified Modelling Language (UML)
used to model object oriented software design
???
1.2 图示

第一栏的Employee就是上文介绍的class;
第二栏(Employee Name,Employee ID)是class的attributes——即Python Variables;
Part of the essential description of data in a class
Each object has its own value for each attribute in its class
The visibility of attributes are private. This means that data is hidden from other objects, which have no direct access to the data of an entity, such as Employee
第三栏是operation——即Python Method。
The common behaviour shared by all instances (objects) of the class
Services that objects of a class can provide to other objects
The visibility of operations are public, if they are designed to be accessible to other objects. Operations of an object can be private or protected if they are only to be used by the object itself or a group of objects, respectively
1.3 Create a Class
class Person:
def __init__(self, fname, lname): //attribute
self.fistname = fname
self.lastname = lname
def printname //operation
print(self.firstname, self lastname)
x = Person('John', 'Doe') //object
x.printname() //call operation__init__()
- All classes have a function called
__init__(), which is to assign values to object properties, or other operations when the object is being created
有点类似于C#中的构造函数!
self(or other)
The self parameter is a reference to the current instance of the class, and is used to access variables that belongs to the class.
The self parameter could be given any name, e.g. mysillyobject or abc, but it has to be the first parameter of any methods in the class
class Person:
def __init__(abc, fname, lname):
abc.fistname = fname
abc.lastname = lname
def printname
print(abc.firstname, abc lastname)
x = Person('John', 'Doe')
x.printname()2. Python:Function vs. Methods
2.1 Python function
- User-Defined Functions
def add(a,b):
return a + b
add (3,-3)- Built-in Functions
比如print
2.2 Python Methods
Python method is a function attached to an object.
Python method is called on an object.
class vehicle:
def __init__(self,color):
self.color = color
def showcolor(self):
print(f"The color is {self.color}")
car = vehicle("red")
car.showcolor()这里面的showcolor就是Method
3. Class Diagram
3.1 Association
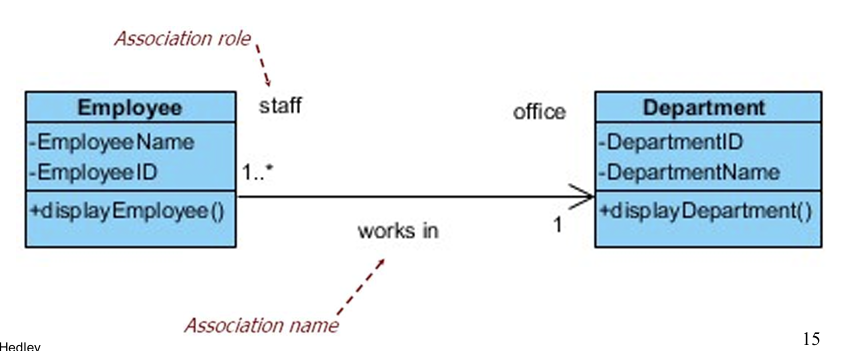
- An abstraction which connects two classes
- Represents the possibility of a logical relationship or connection between objects of one class and objects of another
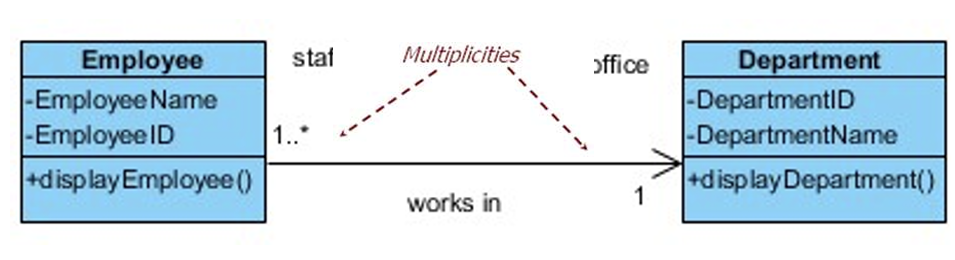
3.1.1 Multiplicity
Associations have multiplicity
Multiplicity is the range of permitted cardinalities of an association
−One to one association
−One to many association
−Many to one association
−Many to many association
Represent enterprise (or business) rules, for example: −Any bank customer may have one or more accounts
−A sole account is for one, and only one, customer
−A joint account(共同账户) has two customer holders
Example:Many to one association
3.1.2 Message Passing
:place Department object reference (held in the attribute, Department) in the Employee class, thus the Employee object can communicate and send message to the Department object. i.e. calling the Department object’s method, display Department(), but not vice versa
−Sending object: Employee object
−Receiving object: Department object
前提:是Employee调用Department里的方法!
4. Inheritance
Add inheritance structures when: (什么时候用继承)
− Two classes are similar in most details (i.e. generalisation概括化), but differ in some respects (i.e. specialisation专业化)
- In behaviour (operations or methods)
- In data (attributes)
- In associations with other classes
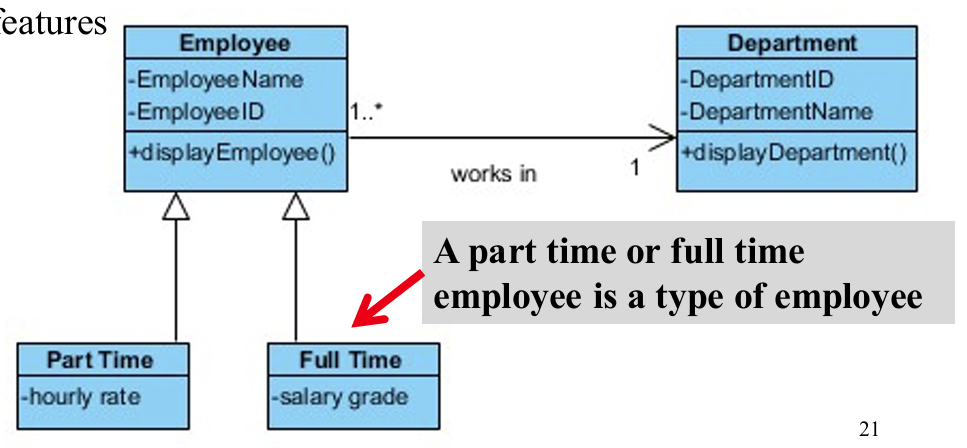
4.1 inheritance relationship
Apply the “is-a” rule, denoted as a hollow triangle.
tips: “is a”就是父类和子类的关系。
Example scenarios:
- Borrower “is a” Library User
- Student “is a” Borrower
- Film “is a” Recorded Item
4.2 父类子类别称
父类:
- Abstract class
- super class
- general class
子类:
- concrete class
- sub-class
- specialised class
4.3 Example
A part-time employee ‘is a’ type of employees
concrete class (subclass): shared the general features from the superclass, but individual subclasses have their own specialised features.
4.4 代码实现
4.4.1 Parent class
class Person:
def __init__(self,fname,lname):
self.fname=fname
self.lname=lname
def printname(self):
print(self.fname,self.lname)4.4.2 Child class
To keep the inheritance of the parent's __init__() function, add a call to the parent's __init__() function.
4.4.2.1 all the methods and properties from its parent
子类调用父类方法:(super class).(Method)
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,fname,lname):
Person.__init__(self,fname,lname)Use super() function that will make the child class inherit all the methods and properties from its parent:
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,fname,lname):
super().__init__(fname,lname)//用super,在这的括号就不用self了4.4.2.2 adding additional attributes/methods
Using self.attribute_name
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,fname,lname):
super().__init__(fname,lname)
self.graduationyear = 2019pass the new attribute when creating objects
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,fname,lname,year):
super().__init__(fname,lname)
self.graduationyear = year
x = Student('John','Smith',2020)Using method_name(self) to add a new method
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,fname,lname,year):
super().__init__(fname,lname)
self.graduationyear = year
def welcome(self):
print('welcome to',self.fname,self.lname,"to the class of",self.graduationyear)
x = Student('John','Smith',2020)
x.welcome()4.4.2.3 Method overriding
the child class implements the code different from the parent class
class Parent:
def __init__(self):
self.value = 5
def get_value(self):
return self.value
class Child(Parent):
def get_value(self):
return self.value + 14.4.2.4 Method overloading
the method name is same but with different number of parameters
class computer:
def area(self,x = None,y = None):
if x != None and y != None:
return x * y
elif x != None:
return x * x
else:
return 0
d = computer()
print(d.area(3,4))
print(d.area(3))
print(d.area())the method name is same but with the parameters of different types
class OverloadDemo:
def method(self,a):
print(a)
obj = OverloadDemo()
obj.method(3.14)
obj.method('sherry')
obj.method(7)5. Aggregation vs Composition
5.1 vs Association
- Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent. Example: Class (parent) and Student (child). Delete the Class and the Students still exist.
Aggregation 指子类可以脱离父类而存在
- Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independent of the parent. Example: House (parent) and Room (child). Rooms don't exist separate to a House.
Composition 指子类不能脱离父类而存在
Aggregation和Composition 是特殊类型(具体类型)的Association。
5.2 a whole part relationship and “has a” rule
Aggregation represents a whole-part relationship
Composition represents a whole-part relationship with a stronger ownership of the part
Each part may belong to only one whole at a time
When the whole is destroyed, so are all its parts
Has a one to many relationship
Model aggregation/composition applying the “has-a” rule (or “has-an”)
- Example scenarios:
Vehicle “has an” Engine
Committee “has a” tutor (as member)
A class has a student
5.3 hollow diamond and solid diamond
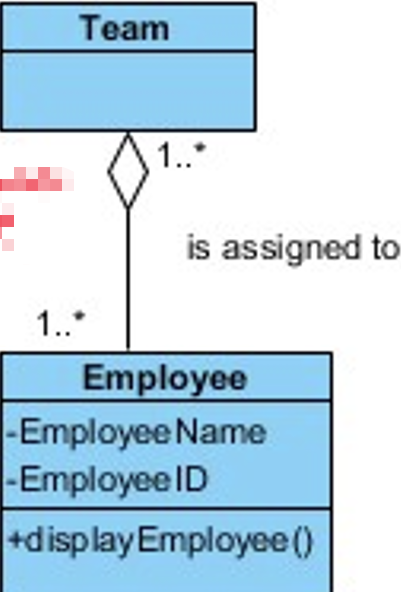
5.3.1 Aggregation Denoted as a hollow diamond
− Multiplicity can be represented at both ends of the line. The multiplicity of the composite end may be more than one (many to may relationship).
Aggregation 可以是many to many的关系。
Example:
- A team ‘has a’ number of employee to work in;
- An employee can work in more than one team;
这里就是说 hollow diamond 两端可以指向多个对象(无论是子类还是父类)
- however, if a particular team is removed, the employees working in that team will still be able to work for other teams.
Aggregation 特性,父类被移除子类还可以存在
5.3.2 Composition uses the filled or solid diamond.
The multiplicity of the composite end must be at most one (one to many relationship). The larger composite solely owns the part. The part cannot have another owner. The symbol shows strong ownership.
Composition 只能是一对多的关系。只能有一个父类(owner)。
Example:
- A branch(部门) ‘has a’ number of employees working in;
- a employee can only work in a branch and if a particular branch closes,
one to many!!!
- all employees work in that branch will be no longer employed.
父类(owner)消失,子类不能存在。
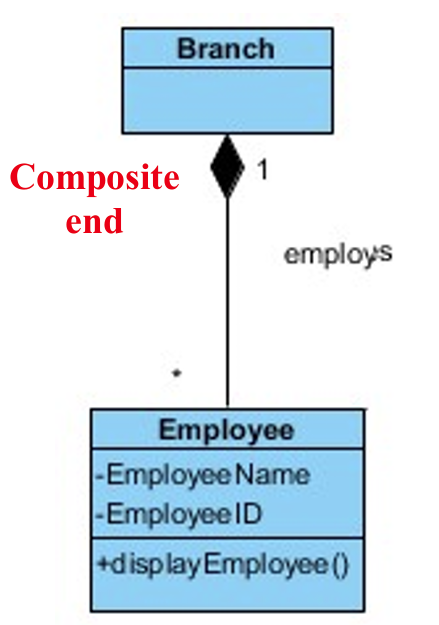
5.3.3 Example
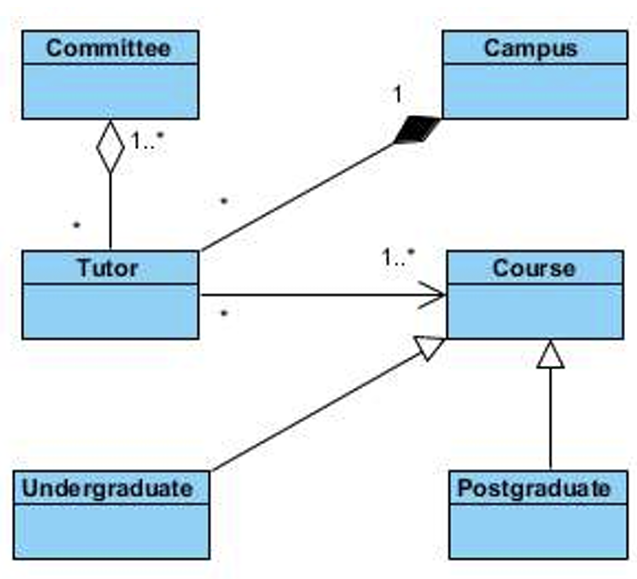
a tutor can only teach in one of the campuses, but could sit in more than one committee and teach many courses, which include undergraduate or postgraduate courses.

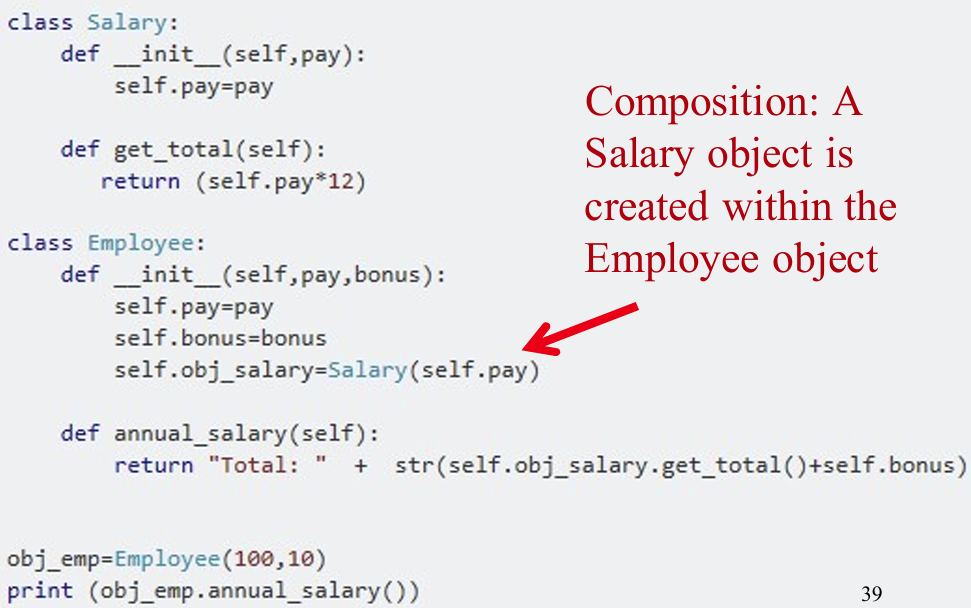
6. Design Model
6.1 Data types
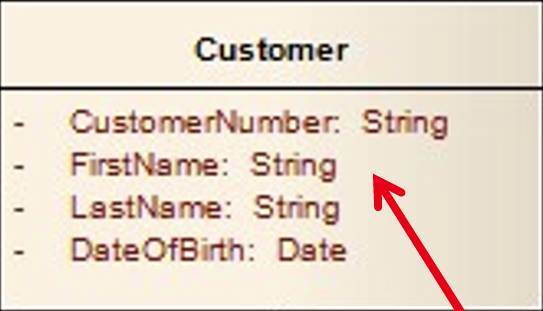
attributes Provide data types for existing attributes: String (e.g. characters), Integer (whole numbers), double (numbers with decimal places), Boolean (True or False) etc.
6.2 derived attributes
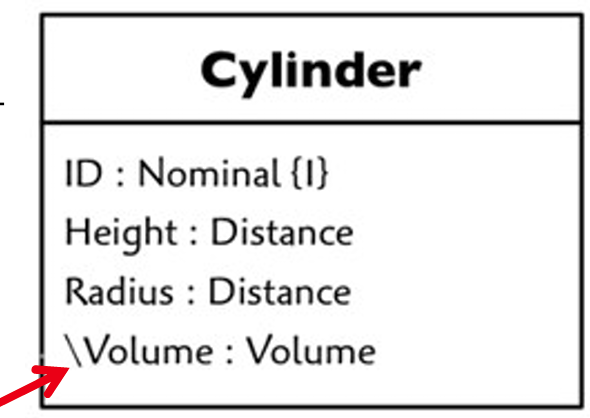
derived attributes the value returned are derived from other attributes.
下面代码中的 get_full_name 就是上图说的派生属性。
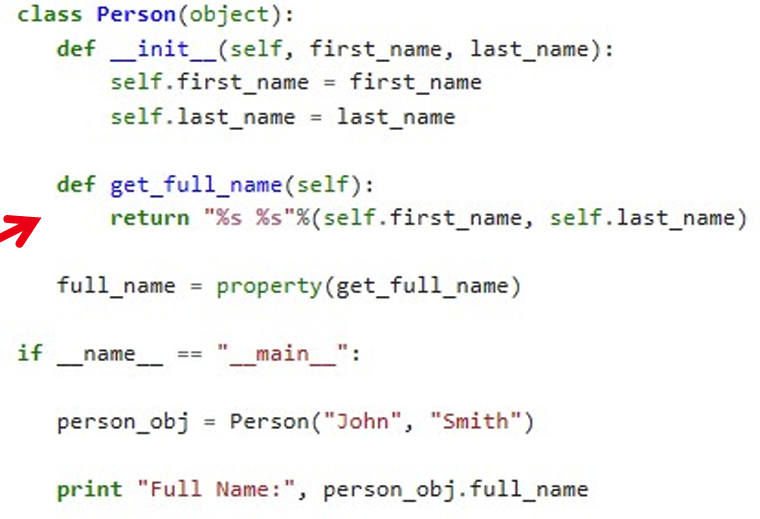
6.3 operation
- Primary operations
Get operation: to get the value of an attribute
Set operation: to set/change the value of an attribute
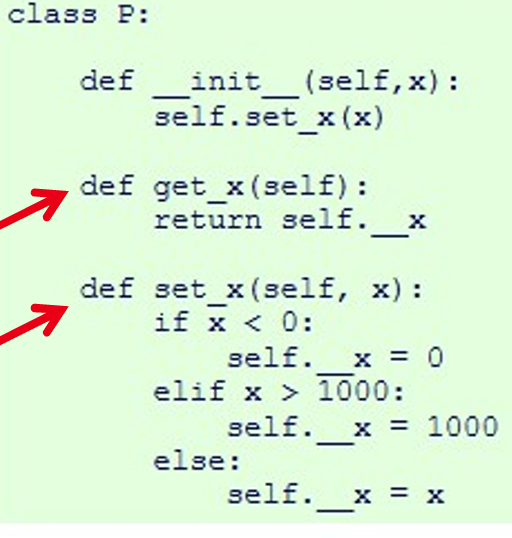
input and return:
Input arguments (or parameters): names and their data types if required
Return data type for the value obtained from executing an operation if required
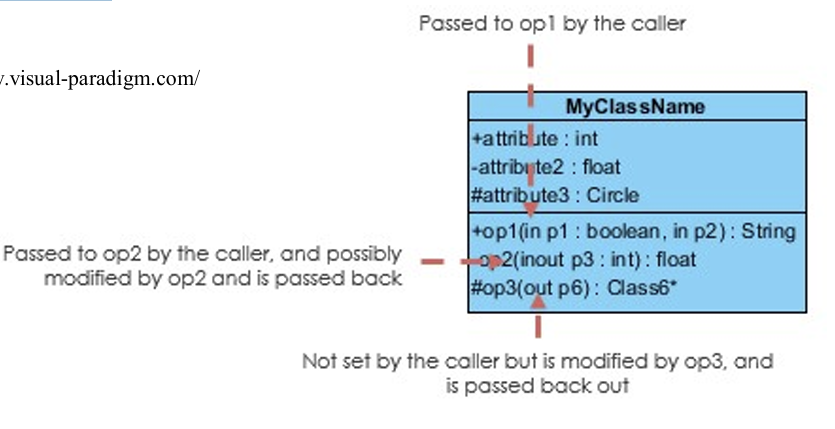
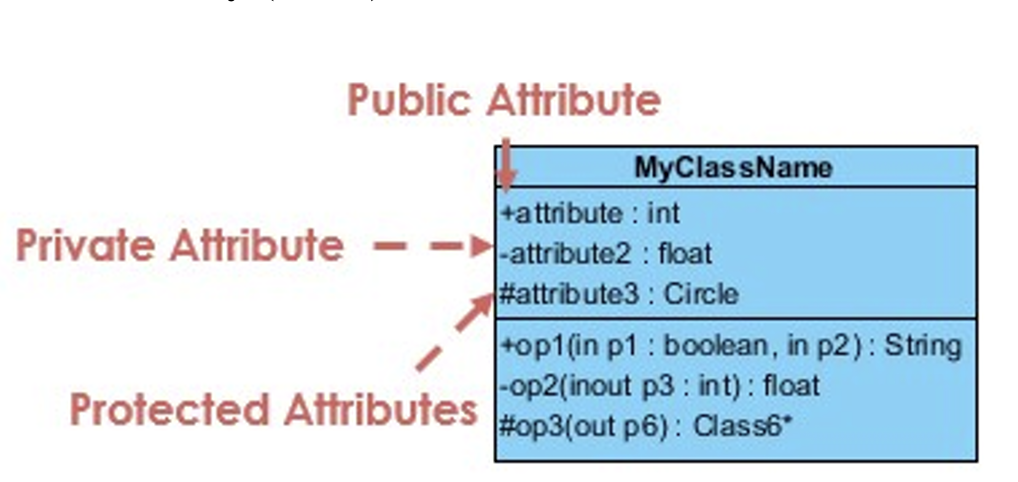
6.4 Visibility
- Private (-): only directly accessible by an instance of the class that includes them (本类和实例)
- Public (+): only accessible by an instance of any class
- Package (~): only directly accessible by an instances of the class in the same package (程序包)
- Protected (#): only accessible by an instance of the class that includes them or a subclass (本类和子类实例)
Private: indicated in two underscores__
class cup: def __init__(self): self.__content = None def fill(self,ber): self.__content = ber def empty(self): self.__content = NonePublic: Python have no mechanism that effectively restricts access to any instance variable or method. All members in a Python class are public by default. Any member can be accessed from outside the class environment. This differs in other languages, such as Java, which has no public attributes.(Python中属性默认公开)
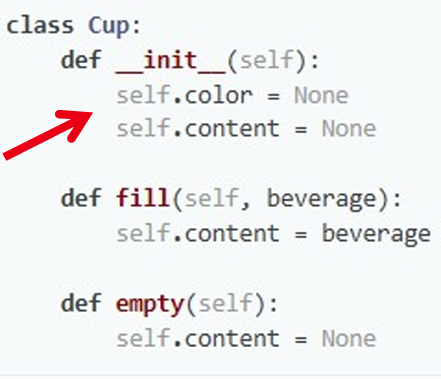
上面color和content默认是public。
- Protected: accessible within super-class and sub-classes; indicated in one underscore _
class cup:
def __init__(self,color):
self.color = None
self._content = None
def fill(self,ber):
self._content = ber
def empty(self):
self._content = None上面content就是Protected的。
